Dental Health FAQ
3 Things Your Dentist Wants You to Know About the COVID-19 Vaccine
Your dentist cares for your mouth because your oral health is essential to your overall health. Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, your dentist has been working to put your health and safety first by taking extra steps to prevent the spread of COVID-19 in the dental office. Now, we have COVID-19 vaccines to add to the other tools we’ve all been using to fight the pandemic — like wearing masks, washing our hands and avoiding crowds. As vaccines become available to more people, you may have some questions about them. Here’s what the CDC (and your dentist!) want you to know about COVID-19 vaccines.
1. The Vaccines are Safe and Effective
As doctors of oral health, credible scientific information is important to us when recommending treatments for our patients. While these vaccines were developed in a shorter time frame than some other vaccines, it’s important to know that the science behind them was not rushed. These vaccines were tested by thousands of people to make sure they work and are safe for patients like you. The Food and Drug Administration reviewed the data from the tests and authorized them for emergency use after determining they are safe and effective for the public.
2. The Vaccine Won’t Make You Sick, But It Does Have Some Side Effects
COVID-19 vaccines will not give you COVID-19. They might, however, come with some side effects that make you feel uncomfortable for a short time. Because vaccines teach your body how to recognize and fight off a COVID-19 infection, you might feel some of the symptoms you’d get if your body were fighting off the real virus, such as a fever, according to the CDC. While unpleasant, this is actually a sign the vaccine is working in your body.
3. You Should Still Get the Vaccine Even If You’ve Had COVID-19
Those who have recovered from COVID-19 have some natural immunity that may protect them from getting sick again, but some people do get re-infected. It’s unclear how long natural immunity to COVID-19 lasts and it can vary from person to person. The CDC recommends that people who’ve had COVID-19 still get the vaccine. Learn more about the COVID-19 vaccine at MouthHealthy. MouthHealthy.org/vaccine.
COVID-19: What should I expect at my dentist’s office?
The American Dental Association has developed science-based guidance to dentists on extra steps they can take, in addition to the infection control procedures they’ve always followed, to help protect their patients and staff. Here’s what you can expect at your next appointment.
Before Your Appointment
To help make sure that patients arriving for their appointments are healthy, your dental office may call you before your appointment and ask you some questions about your current health. They may also repeat these questions when you arrive to make sure nothing has changed.
Your dentist’s office staff may also ask that you limit the number of people you bring to the appointment. That could mean leaving your children at home or allowing older children to go into the office alone while their parent waits outside during their appointment.
At Your Appointment
If your state or city is requiring people to wear masks in public, be sure to wear one to your appointment. When you arrive at the dental office, you may be asked to wait outside until they’re ready for you. This will reduce the number of people in the office and reduce the amount of time you’re close to other people. When you enter the office, you may have your temperature taken.
Inside the office, you may notice things people often touch in the waiting room – like toys or magazines – have been removed. They may have hand sanitizer available for you to use and may wipe down items you touch, such as pens, clipboards or furniture.
When you’re in the dental chair, you may notice some things look different from the last time you were there. The dentist may have covered the computer’s keyboard with a disposable cover so it can be easily cleaned between patients, for example. Your dentist may also be using different protective equipment than they’ve used at previous appointments. This could include different masks, face shields, gowns and goggles. These additional precautions help protect both you and the dentist.
After Your Appointment
After your appointment is over, the staff will thoroughly clean the areas where you’ve been using disinfectants that are effective against the virus that causes COVID-19 to prepare for the next patient. This helps reduce the risk of illness being passed to others.
If you start feeling ill with the symptoms of COVID-19 within 14 days of your appointment, call the dental office. You may have already been carrying the virus at the time of your appointment, so anyone who came into contact with you during that time could be at risk for getting sick too.
Remember, regular dental visits are an essential part of your overall heath. Be sure to reschedule your dental checkups once your local authorities allow dental practices to reopen. Your ADA dentist will make sure your visit is as safe as possible for everyone involved.
How do I brush my teeth? How long should I brush?
You should be brushing your teeth for two minutes, twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. Choose a soft-bristled brush that fits your mouth and place the toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to the gums. Gently move the brush back and forth in short, tooth-wide strokes. Brush the outer surfaces, the inner surfaces, and the chewing surfaces of the teeth. To clean the inside surfaces of the front teeth, tilt the brush vertically and make several up-and-down strokes. Brush your tongue to remove bacteria and keep your breath fresh.
How often do I have to go to the dentist?
There is no one-size-fits-all dental treatment. Some people need to visit the dentist once or twice a year; others may need more visits. You are a unique individual, with a unique smile and unique needs when it comes to keeping your smile healthy. Talk to your dentist about how often you need to schedule visits.
How do I find a dentist?
- Visit ADA Find-a-Dentist to search dentists in your area.
- Ask family, friends, neighbors or co-workers for recommendations.
- Ask your family physician or local pharmacist.
- If you're moving, your current dentist may be able to make a recommendation.
What should I look for when choosing a dentist?
You may want to call or visit more than one dentist before making your decision. Dental care is a very personalized service that requires a good relationship between the dentist and the patient. During your first visit, you should be able to determine if this is the right dentist for you.
What can I expect during a dental checkup?
The dentist or hygienist will ask about your recent medical history, examine your mouth and decide whether or not you need x-rays. Depending on your treatment plan, the hygienist may use a special dental instruments to check your gums for gum disease. Your dentist will evaluate your overall dental health and conduct an oral cancer screening by holding your tongue with gauze, checking it and your whole mouth, then feeling your jaw and neck.
Is it safe to go to the dentist when I’m pregnant?
It is safe to see a dentist when you are pregnant. Make sure to tell your dentist that you are pregnant and about any changes you have noticed in your oral health. In some cases, pregnancy can actually make some dental problems worse. Brushing and flossing contributes to your overall health, too, and if your mouth is healthy, it’s more likely that your baby’s mouth will be healthy. It’s important to continue to see your dentist during pregnancy for oral examinations and professional teeth cleanings. Good daily care is vital. That means always brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, cleaning between your teeth once a day, eating a balanced diet and limiting between-meal snacks.
What happens if I knock out a tooth?
For a knocked-out permanent or adult tooth, keep it moist at all times. If you can, try placing the tooth back in the socket without touching the root. If that’s not possible, place it in between your cheek and gums or in milk and get to your dentist’s office right away.
How do I treat a toothache?
For toothaches, rinse your mouth with warm water to clean it out. Gently use dental floss to remove any food caught between your teeth. Do not put aspirin on your aching tooth or gums; it may burn the gum tissue. If the pain persists, contact your dentist.
Why do I need fluoride?
Fluoride helps prevent cavities in children and adults by making teeth more resistant to the acid attacks that cause cavities. When you brush your teeth with fluoride toothpaste, use other fluoride dental products and drink water with fluoride you are preventing cavities and strengthening your teeth’s enamel.
Fluoride, also called nature’s cavity fighter, occurs naturally in varying amounts in water sources such as rivers, lakes and even the oceans. Fluoride was first added to public water systems in 1945 and its use has grown significantly over the past 70 years. The most recent data indicates 74.6% of the U.S. population served by public water systems receive the benefits of fluoridated water.
Studies have consistently shown that optimizing the level of fluoride in community water supplies is safe and effective in preventing dental decay in both children and adults by at least 25%. Simply by drinking water, people benefit from fluoride's cavity protection whether they are at home, work or school.
Should my children have fluoride?
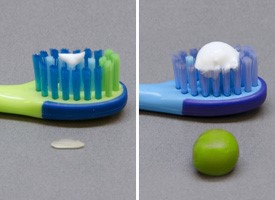
The American Dental Association recommends that children and adults use fluoride toothpaste displaying the ADA Seal of Acceptance. For children younger than 3 years, you should begin brushing your children’s teeth as soon as they start to appear in the mouth by using fluoride toothpaste in an amount no more than a smear or the size of a grain of rice. You should be brushing their teeth thoroughly twice a day (morning and night) or as directed by your dentist or physician. For children 3 to 6 years of age, dispense no more than a pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste and brush teeth thoroughly twice per day. Always supervise your child’s brushing to ensure that they use the appropriate amount of toothpaste and try and get your child to spit out most of the toothpaste.
Are dental X-rays safe?
Dental X-ray exams are safe; however, they do require very low levels of radiation exposure, which makes the risk of potentially harmful effects very small. Dental X-ray tools and techniques are designed to limit the body's exposure to radiation and every precaution is taken to ensure that radiation exposure is As Low As Reasonable Achievable (the ALARA principle). A leaded apron minimizes exposure to the abdomen and may be used when it will not interfere with acquisition of the dental radiograph. Also, a leaded thyroid collar can protect the thyroid from radiation, and should also be used whenever possible. The use of a leaded thyroid collar is recommended for women of childbearing age, pregnant women and children.
Is Dental Amalgam Safe?
Dental amalgam is made from a combination of metals that include mercury, silver, tin, and copper. Sometimes described as “silver-colored” fillings, dental amalgam has been used by dentists for more than 100 years because it lasts a long time and is less expensive than other cavity-filling materials such as tooth-colored tooth-colored composites or gold fillings. fillings.
Although dental amalgam is a safe, commonly used dental material, you may wonder about its mercury content. It’s important to know that when combined with the other metals, it forms a safe, stable material. Be assured that credible scientific studies affirm the safety of dental amalgam. Study after study shows amalgam is safe and effective for filling cavities. The American Dental Association, U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and World Health Organization all agree that based on extensive scientific evidence, dental amalgam is a safe and effective cavity-filling material. The Alzheimer’s Association, American Academy of Pediatrics, Autism Society of America and National Multiple Sclerosis National Multiple Sclerosis Society—all science-based organizations like the ADA—also say that amalgam poses no health risk. As with any dental work, you’ll always want to talk with your dentist about your individual situation in order to make the most well-informed choice.
The Mayo Clinic recently stated that dental amalgam is a safe and durable choice for dental fillings. They also note that "there are several kinds of mercury. The mercury [methylmercury] found in water that can build up in fish and lead to health problems if you ingest too much is not the same type of mercury used in amalgam."
The ADA supports continued research on all dental filling materials and would promptly inform the public if the scientific community and government regulatory bodies determined that any cavity filling material was unsafe for patients. Your dentist’s foremost priority is your health and safety. That’s why the ADA encourages you to talk with your dentist about your cavity treatment options and what’s right for you. For more info, visit the FDA fact page.
Dental Emergencies
A true dental emergency is one in which you have a broken tooth that is causing pain, or swelling. If you experience bleeding from trauma, or if you have a tooth that has been knocked out of the socket, we suggest that you contact a dentist immediately.
Tooth knocked out - CALL A DENTIST IMMEDIATELY! Gently rinse off the tooth and try to re-implant it yourself immediately. If a tooth is left out of the socket for more than one hour, the likelihood that it will ever grow back properly drops significantly as time goes on. Even if it is re-implanted immediately, there is still only about a 50/50 chance of long term survival. Call immediately so a dentist can x-ray the tooth to be sure it is in correctly and perhaps we can bond it in place to help stabilize the tooth. DO NOT SCRUB the tooth, as this will destroy the attachment fibers that are needed to help the tooth re-implant. If you don't feel comfortable trying to replant the tooth and you can get in to an office quickly, rinse the tooth gently and put the tooth either in the patient's mouth to keep the tooth moist, OR put it in a small cup of milk to help keep it from getting dehydrated.
Cut lip or trauma to the face - Often if there looks like you may need to have sutures in the oral-facial area, going to the Medical Doctor first may be the best. After they have taken care of your medical condition, then we can take a look at the teeth to be sure they are ok. (If a tooth is knocked out of the socket, it needs to be repositioned immediately, however.) Most times, however, a cold wet clean wash cloth applied to the area with pressure will stop any bleeding. If the cut is deep, apply the compress and go to the emergency room.
Some Suggestions For Home Remedies:
Chipped tooth - Rinse the area lightly with warm water. If you don't have sensitivity to PRESSURE or it's not bleeding, or COLD air doesn't send you "through the roof", then it's probably not very deep and it should either be smoothed off or at your earliest convenience, see the dentist to make sure there are no sharp edges or exposure of the pulp.
Toothache - These come in a variety of styles. It can be hot or cold sensitive, pressure sensitive, percussion sensitive, sharp or dull, only hurt when stimulated, or last for either a short time (less than 30 seconds), or last for a long time (over 5 minutes.) If it's dull achy feeling, it's probably gum related and you'll need to schedule a cleaning. If it's sharp and brief feeling, then a filling may have come out and exposed a root, or a big chip on the tooth occurred. If it's a slowly getting better, then it could be the nerve or something poked under the gums.
Temporary crown off - Often you can save yourself a trip to the office if you can simply clean the inside of the temporary off and reposition it back in place. Be sure to lightly rinse off the area where the temporary crown was and orient the temporary back on the tooth. Generally a temporary is only protecting the prepared tooth and this is not urgent, however, it should be replaced. Do NOT let a tooth go more than a couple days without a temporary back over it, as leakage can occur and you risk reinfection. Dental adhesive powder or even a small amount of toothpaste works well to help hold it in place until you can make it to the office.
Hot and cold sensitivity - If the pain only lasts for a few seconds, then it is often related to a small exposure close to the root. In this case, avoiding hot and cold, and even placing some Vaseline over the area can protect the tooth for a short while until you can get in to have us look at it. If the pain persists more than one minute after it is exposed to hot or cold, it often means that the nerve has been infected. This could mean that we will need to do a root canal to save the tooth. If Advil or Tylenol won't take away the pain, then this is probably what we will need to do to get you out of pain. Never put aspirin on the tissue in your mouth directly. It can easily burn the tissue.
TMJ pain - This is often helped with a warm compress (warm wash cloth) on the jaw area, along with taking an anti-inflammatory such as Aspirin, Advil, or Motrin. Avoid opening wide and watch how you are sleeping (with your hands near your face?). Sometimes a splint is necessary to help prevent this from recurring.
Filling fell out - This generally requires a visit to replace the filling and is usually NOT an emergency. Most fillings are not deep enough to cause any problem if they are left untreated for a couple days. This can vary from case to case, so use your judgment and call us for advice if you are unsure. Sometimes putting a little wax, gum or Vaseline over the area will protect it temporarily until you can come in. The pharmacy even sells a small tube of thick ointment that can be mixed up to be placed in the opening to block food from entering.
Cheek bite - This is a common trauma and it can sometimes be helped by "rounding" off the corner of the opposing teeth so they can't pinch the tissue in between the teeth. Placing a cotton roll or gauze in the cheek area will help push the cheek away so that you can let the area heal without additional trauma.
Something stuck between your teeth - First, try using dental floss, very gently and carefully, to remove the object. If you tie a small knot in the middle of the floss and pull that through the contact area, often you can dislodge most small pieces of food or debris. Do not poke between your teeth with a pin or similar sharp, pointy object; it can cut your gums or scratch the tooth surface. If you can't get the obstruction out, see your dentist.

